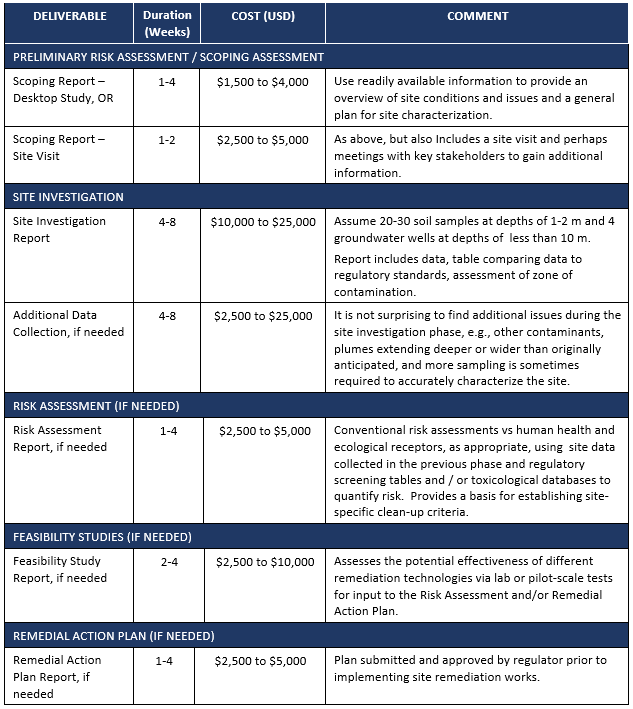
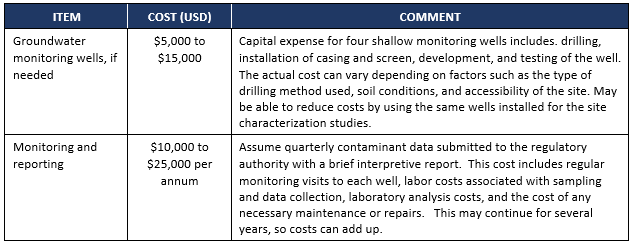
Capital costs:
- Very Low ≤ $15,000;
- Low >$15,000 to ≤ $30,000;
- Moderate $30,000 to $100,000;
- High >$100,000
Annual operating costs:
- Very Low ≤$10,000;
- Low $10,000 to ≤$25,000;
- Moderate $25,000 to $100,000;
- High >$100,00
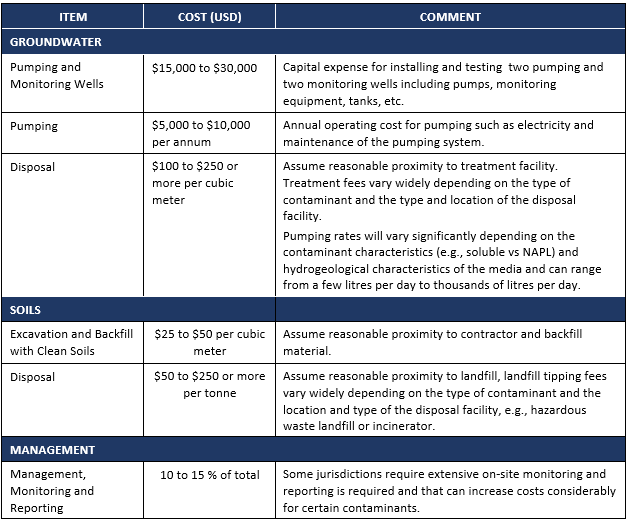
Removal and Disposal
Costs for removal and disposal are highly variable and may be cost prohibitive, depending upon volumes of contaminated media to be removed, transport costs, and tipping, plus destruction and/or disposal fees associated with different types of contaminants.
Costs for Removal and Disposal
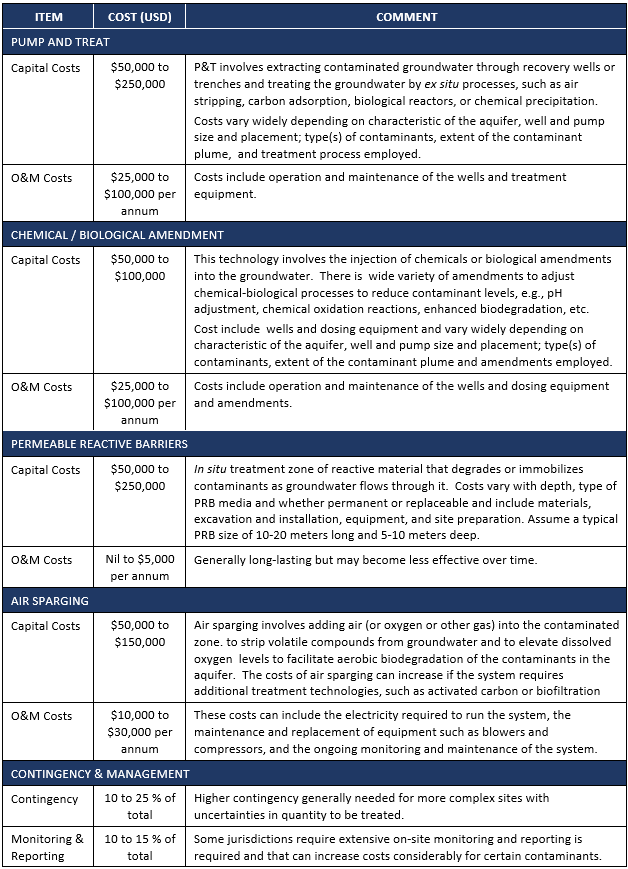
On-Site Treatment
Capital costs for on-site treatment technologies are higher than approaches described above for off-site disposal. These additional costs are associated with the equipment and installation costs required for the ex situ or in situ treatment technologies.
They may however be balanced by the lower operating costs, e.g., in cases where off-site disposal costs are very expensive.
Typical Costs for Selected On-Site Groundwater Remediation Technologies
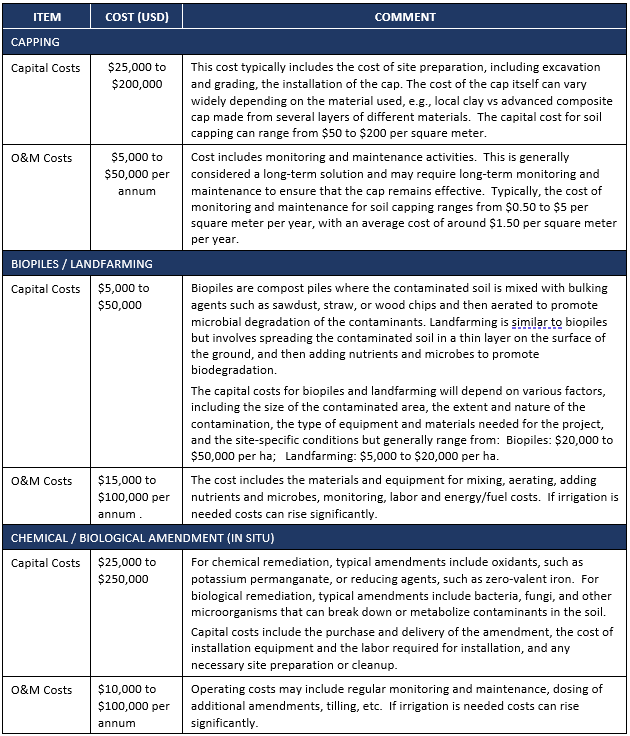
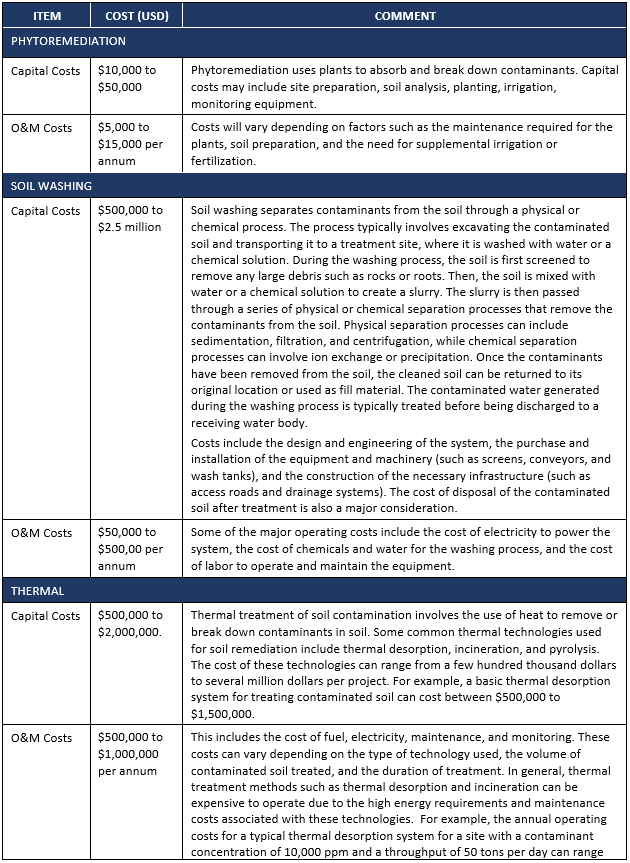
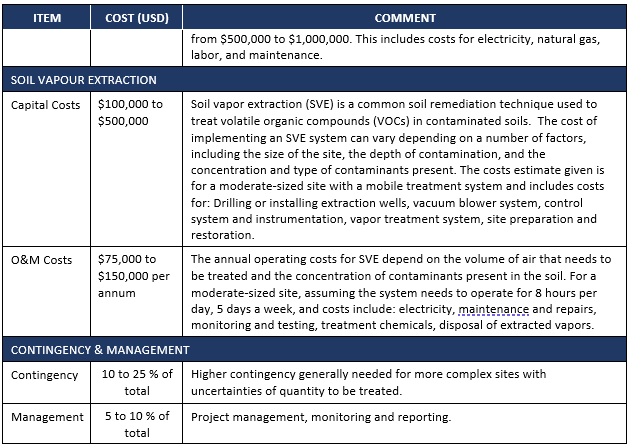
Typical Costs for Selected On-Site Soil Remediation Technologies
 Questions related to remediation? Feel free to contact me, any of my Inogen Alliance colleagues across the globe. We are here to help you.
Questions related to remediation? Feel free to contact me, any of my Inogen Alliance colleagues across the globe. We are here to help you.
- Is Your Business Compliant with HSE Regulations? Take Our Quiz to Find Out! - September 16, 2024
- Duty of Care: What it Is and What it Means to Companies Operating in the GCC? - January 28, 2024
- Free E-Book:Health, Safety, and Environment Regulatory Review – United Arab Emirates: An Overview of Federal Requirements - July 5, 2023